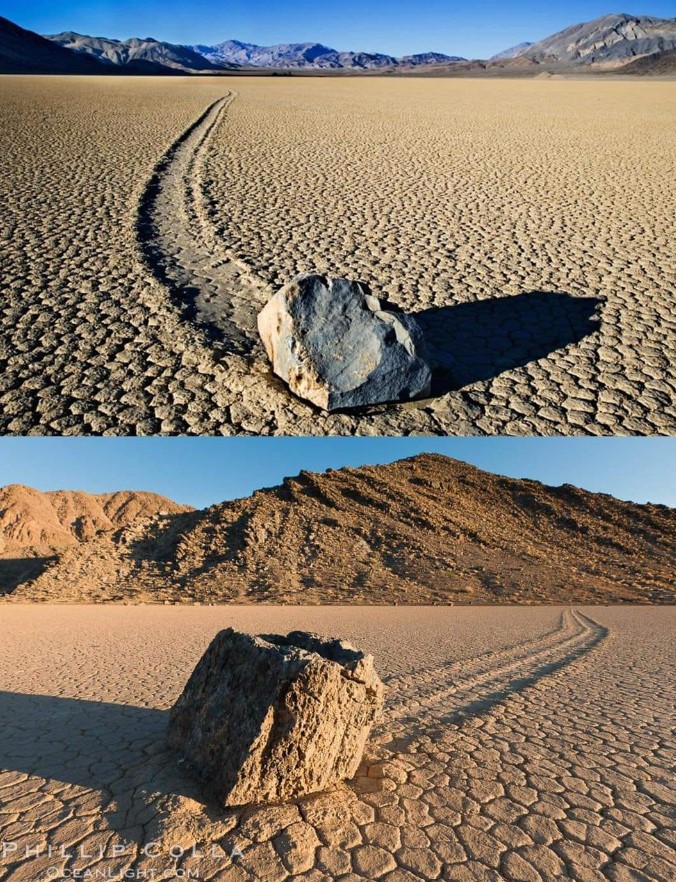
In California’s Death Valley, large stones move across the desert floor, leaving long trails behind them. Despite many studies, no one has directly observed how these stones move.
The mystery of Death Valley’s “sailing stones” has long stumped visitors to the national park and scientists alike. How do rocks at an area called Racetrack Playa, some larger than a microwave, move several yards across the desert floor, leaving tell-tale trails in the sand?
Ralph Lorenz, a planetary scientist at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, may have cracked the case at his kitchen table.
Lorenz employed a tried-and-true method for testing his nascent idea: the kitchen-table experiment. “I took a small rock, and put it in a piece of Tupperware, and filled it with water so there was an inch of water with a bit of the rock sticking out,” he says.
“I put it in the freezer, and that then gave me a slab of ice with a rock sticking out of it.” He flipped the rock-ice hybrid upside down and floated it in a tray of water with sand on the bottom. By merely blowing gently on the ice, he realized, he could send the embedded rock gliding across the tray, scraping a trail in the sand as it moved. After decades of theoretical calculations by countless scientists, the answer seemed to be sitting on his tabletop.
More Information :
Also read this beautiful story : This bird creates a FAKE entrance to its nest to trick predators